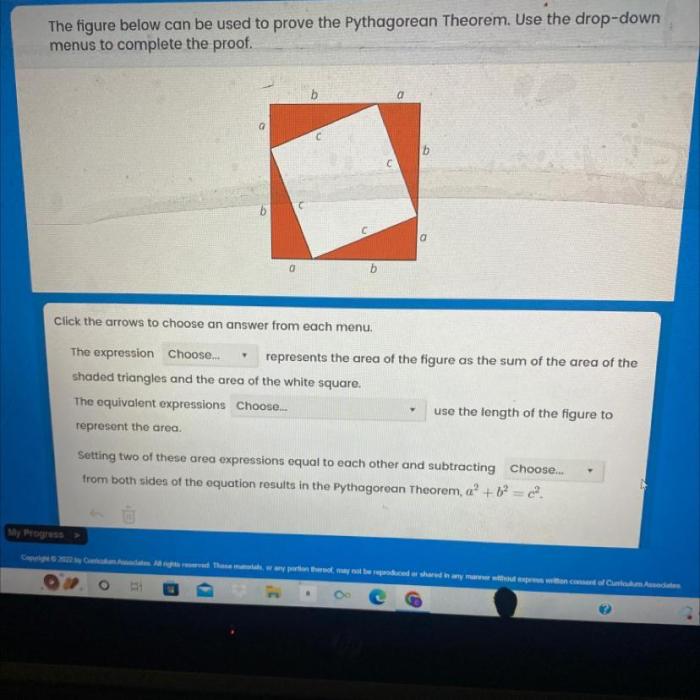
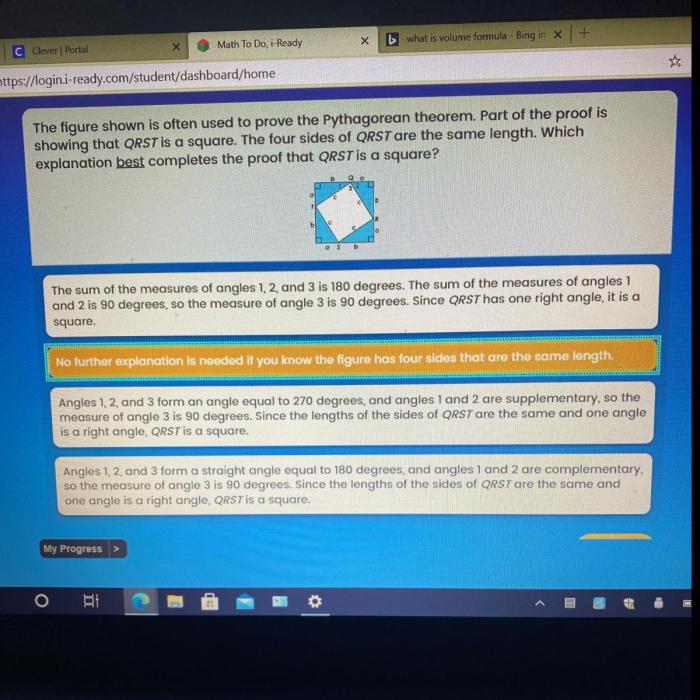
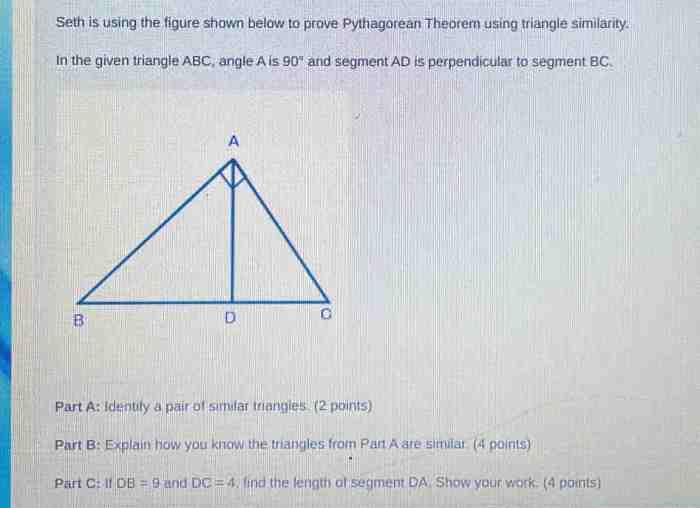
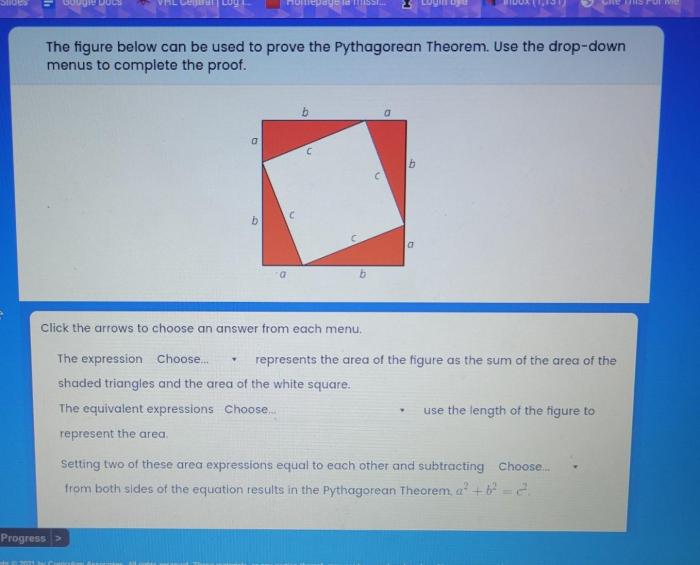
The figure shown is often used to prove the Pythagorean theorem, a fundamental concept in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. This theorem has significant applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and surveying.
Understanding the figure and its role in proving the theorem is essential for comprehending the theorem’s significance and practical implications.
This Artikel will delve into the Pythagorean theorem, the figure used to prove it, alternative methods of proof, and its historical context. It will also explore applications of the theorem in different fields, providing a comprehensive overview of this important mathematical concept.
The Pythagorean Theorem: The Figure Shown Is Often Used To Prove The Pythagorean
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental theorem in geometry that states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
In other words, if a, b, and care the lengths of the sides of a right triangle, with cbeing the hypotenuse, then a2+ b2= c2.
The Pythagorean theorem is significant in geometry as it provides a relationship between the sides of a right triangle. It is used extensively in various fields, including architecture, engineering, surveying, and navigation.
The Figure Used to Prove the Pythagorean Theorem
The figure typically used to demonstrate the Pythagorean theorem is a right triangle with sides labeled as follows:
- a: The length of the side opposite the angle A
- b: The length of the side opposite the angle B
- c: The length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle)
The Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem Using the Figure
The Pythagorean theorem can be proven using the following steps:
- Construct a square with side length a+ b.
- Inside the square, construct four right triangles, each with sides a, b, and c.
- The area of the square is ( a+ b) 2.
- The area of each of the four right triangles is ab/2.
- The area of the four right triangles combined is 4( ab/2) = 2 ab.
- The area of the square minus the area of the four right triangles is the area of the four corner squares, each with side length c.
- The area of the four corner squares is 4( c2) = 4 c2.
- Therefore, ( a+ b) 2
2ab= 4 c2.
- Simplifying, we get a2+ b2= c2, which is the Pythagorean theorem.
Alternative Methods of Proving the Pythagorean Theorem, The figure shown is often used to prove the pythagorean
There are several alternative methods of proving the Pythagorean theorem, including:
- Algebraic proof:Using the formula for the area of a triangle, A= (1/2) bh, where bis the base and his the height, the Pythagorean theorem can be derived algebraically.
- Geometric proof:Using similar triangles, the Pythagorean theorem can be proven geometrically.
Applications of the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem is widely used in various fields, including:
- Architecture:Determining the length of roof rafters, calculating the height of buildings, and designing floor plans.
- Engineering:Calculating the strength of beams, bridges, and other structures.
- Surveying:Measuring distances and determining the elevation of land.
- Navigation:Determining the distance between two points on a map or chart.
Historical Context of the Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem is attributed to the Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who lived in the 6th century BC. However, there is evidence that the theorem was known to Babylonian mathematicians centuries earlier.
Pythagoras is said to have discovered the theorem while studying the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. The theorem has since become one of the most fundamental and well-known theorems in mathematics.
FAQ Section
What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
How is the figure used to prove the Pythagorean theorem?
The figure used to prove the Pythagorean theorem is a square constructed on the hypotenuse of a right triangle. The areas of four smaller squares within the larger square represent the squares of the lengths of the sides of the triangle, demonstrating the theorem’s relationship.
What are some applications of the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem has applications in architecture, engineering, surveying, and other fields where precise measurements and calculations are required. For example, it can be used to determine the height of a building, the distance between two points, or the area of a triangular plot of land.