Lesson 1.5 displaying quantitative data histograms – Lesson 1.5: Displaying Quantitative Data Histograms delves into the realm of data visualization, exploring the power of histograms to represent and analyze quantitative data. Histograms provide a graphical representation of data distribution, offering insights into central tendencies, variability, and the overall shape of the data.
In this lesson, we will embark on a comprehensive journey into the world of histograms, unraveling their purpose, construction, interpretation, and applications. Through real-world examples and engaging discussions, we will uncover the advantages and limitations of histograms, empowering you with the knowledge to effectively display and analyze quantitative data.
1. Introduction

Quantitative data consists of numerical values that can be measured and analyzed. Histograms are graphical representations that display the distribution of quantitative data by dividing the data into intervals and counting the number of data points in each interval. They are useful for visualizing the shape of a distribution and identifying patterns or trends in the data.
2. Creating Histograms
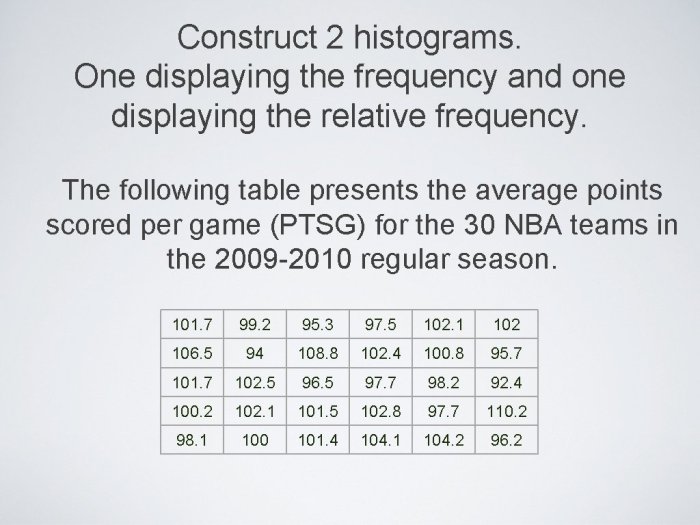
To create a histogram, follow these steps:
- Determine the range of the data and the number of intervals (bins) to use.
- Calculate the width of each bin by dividing the range by the number of bins.
- Count the number of data points that fall into each bin.
- Plot the frequency (count) on the y-axis and the bin intervals on the x-axis.
Different types of histograms include:
- Frequency histograms: Display the count of data points in each bin.
- Relative frequency histograms: Display the proportion of data points in each bin.
- Cumulative frequency histograms: Display the cumulative number of data points up to each bin.
To interpret a histogram, observe the shape of the distribution, the location of the center, and the spread of the data.
3. Applications of Histograms: Lesson 1.5 Displaying Quantitative Data Histograms

Histograms have various applications in different fields, including:
- Data analysis: Exploring data distributions, identifying outliers, and comparing different datasets.
- Statistics: Performing statistical tests, estimating parameters, and making inferences about populations.
- Quality control: Monitoring processes and identifying defects or variations in products.
- Finance: Analyzing stock prices, returns, and risk.
- Healthcare: Studying disease prevalence, treatment outcomes, and patient demographics.
Histograms help in decision-making by providing visual representations of data that can highlight patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
4. Advantages and Limitations of Histograms

Advantages of histograms include:
- Visual representation of data distribution.
- Identification of patterns and trends.
- Estimation of parameters and statistical analysis.
Limitations of histograms include:
- Bin size selection can affect the appearance and interpretation of the histogram.
- Outliers can skew the distribution and distort the histogram.
- Not suitable for displaying categorical data.
Alternative methods for displaying quantitative data include box plots, stem-and-leaf plots, and scatterplots.
5. Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques for creating and analyzing histograms include:
- Using statistical software to generate histograms with customizable options.
- Performing statistical tests on histograms, such as the chi-square test for goodness of fit.
- Creating specialized histograms, such as log-transformed histograms or kernel density estimates.
6. Design Considerations
Guidelines for designing effective histograms include:
- Choosing an appropriate bin size to balance detail and readability.
- Handling outliers by excluding them or using specialized techniques.
- Dealing with missing data by imputing values or excluding incomplete observations.
7. Best Practices
Best practices for displaying quantitative data using histograms include:
- Using clear and concise labels for axes and titles.
- Avoiding over-interpretation of patterns or trends.
- Considering the audience and purpose of the histogram.
Common pitfalls to avoid include:
- Using inappropriate bin sizes or too many bins.
- Ignoring outliers or missing data.
- Overstating the conclusions drawn from the histogram.
Top FAQs
What are the key advantages of using histograms?
Histograms offer several advantages, including their ability to provide a visual representation of data distribution, identify outliers, compare multiple datasets, and facilitate statistical analysis.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid when creating histograms?
Common pitfalls include choosing an inappropriate bin size, ignoring outliers, and failing to consider the underlying assumptions of the data.
How can histograms be used in decision-making?
Histograms can assist in decision-making by providing insights into data patterns, identifying potential risks and opportunities, and supporting data-driven conclusions.