Dna structure and replication worksheet answers key – Delve into the intricacies of DNA structure and replication with our comprehensive worksheet answers key. This guide unlocks the fundamental principles governing the blueprint of life, providing a profound understanding of the molecular machinery that shapes our very existence.
Journey through the double helix structure, deciphering the components of nucleotides and the intricate pairing rules that govern their interactions. Witness the remarkable process of DNA replication, where the genetic code is meticulously duplicated with astonishing precision.
DNA Structure: Dna Structure And Replication Worksheet Answers Key
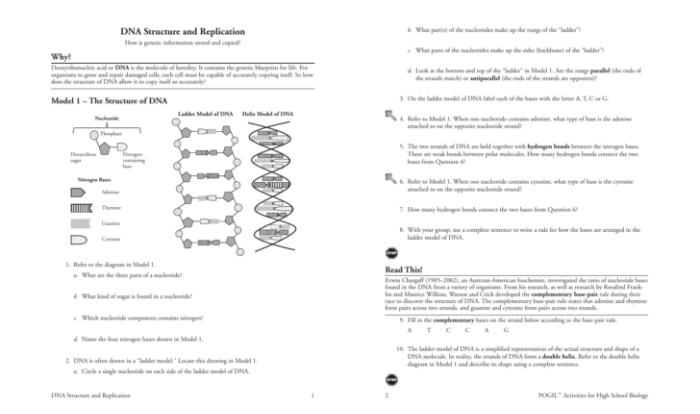
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. It is a double helix structure, consisting of two strands that are twisted around each other in a spiral shape.
Components of a Nucleotide, Dna structure and replication worksheet answers key
Each strand of DNA is made up of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base.
- Sugar molecule:The sugar molecule in DNA is deoxyribose.
- Phosphate molecule:The phosphate molecule in DNA is a negatively charged molecule.
- Nitrogenous base:The nitrogenous base in DNA can be one of four types: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G).
Nitrogenous Base Pairing
The nitrogenous bases in DNA pair with each other in a specific way: A always pairs with T, and C always pairs with G. This is known as the base pairing rule.
Antiparallel Nature of DNA Strands
The two strands of DNA are antiparallel, meaning that they run in opposite directions. This allows the nitrogenous bases on one strand to pair with the nitrogenous bases on the other strand.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, as each new cell needs its own copy of the DNA.
Semi-Conservative Model of DNA Replication
The semi-conservative model of DNA replication states that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication
Several enzymes are involved in DNA replication, including:
- DNA polymerase:DNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands.
- Helicase:Helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix.
- Primase:Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA primers that are needed to start DNA synthesis.
- Ligase:Ligase is the enzyme that joins the newly synthesized DNA strands together.
Process of DNA Replication
The process of DNA replication can be divided into three main steps:
- Unwinding:The DNA double helix is unwound by helicase.
- Base pairing:New nucleotides are added to each strand of DNA by DNA polymerase, following the base pairing rule.
- Joining:The newly synthesized DNA strands are joined together by ligase.
Leading and Lagging Strands
During DNA replication, one strand of DNA is synthesized continuously, while the other strand is synthesized in short fragments that are later joined together. The continuously synthesized strand is called the leading strand, while the strand that is synthesized in fragments is called the lagging strand.
Worksheet Answers Key
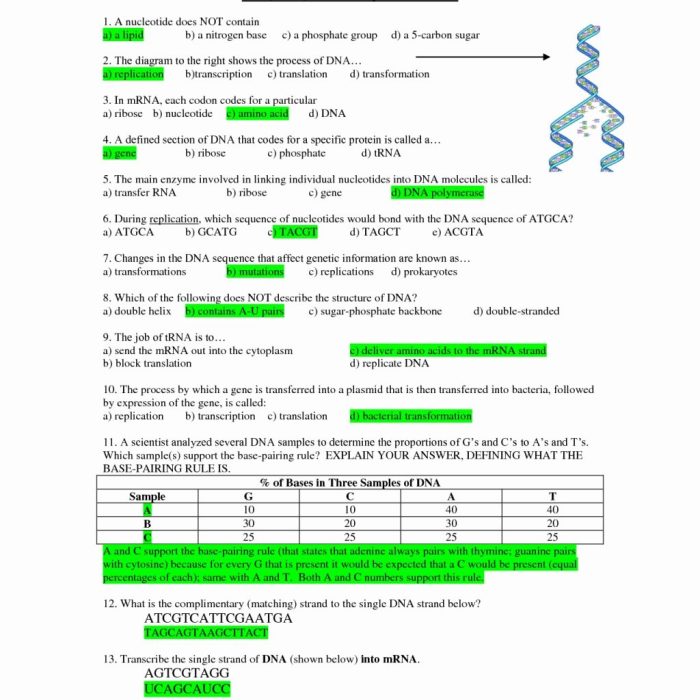
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the structure of DNA? | DNA is a double helix structure, consisting of two strands that are twisted around each other in a spiral shape. |
| What are the components of a nucleotide? | Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate molecule, and a nitrogenous base. |
| What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA? | The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). |
| What is the base pairing rule? | The nitrogenous bases in DNA pair with each other in a specific way: A always pairs with T, and C always pairs with G. |
| What is the semi-conservative model of DNA replication? | The semi-conservative model of DNA replication states that each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. |
| What are the enzymes involved in DNA replication? | The enzymes involved in DNA replication include DNA polymerase, helicase, primase, and ligase. |
| What is the process of DNA replication? | The process of DNA replication can be divided into three main steps: unwinding, base pairing, and joining. |
| What is the difference between the leading and lagging strands? | During DNA replication, one strand of DNA is synthesized continuously, while the other strand is synthesized in short fragments that are later joined together. The continuously synthesized strand is called the leading strand, while the strand that is synthesized in fragments is called the lagging strand. |
Query Resolution
What is the double helix structure of DNA?
DNA consists of two strands twisted around each other to form a double helix, resembling a twisted ladder.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication involves unwinding the double helix, separating the strands, and using each strand as a template to synthesize new complementary strands.