Label the structures on this diagram of a moss and delve into the intricate world of bryophytes. This comprehensive guide unravels the functions, relationships, and diversity of the structures that define these fascinating plants, providing a deeper understanding of their ecological significance and evolutionary history.
Through detailed descriptions, comparative analyses, and interactive tables, this exploration unveils the remarkable adaptations and specialized roles of each structure, showcasing the intricate harmony that sustains the growth and development of mosses.
Label the Structures on the Diagram
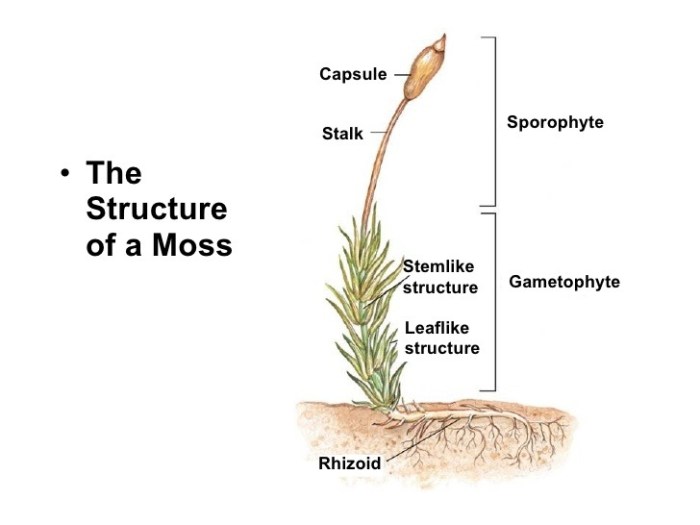
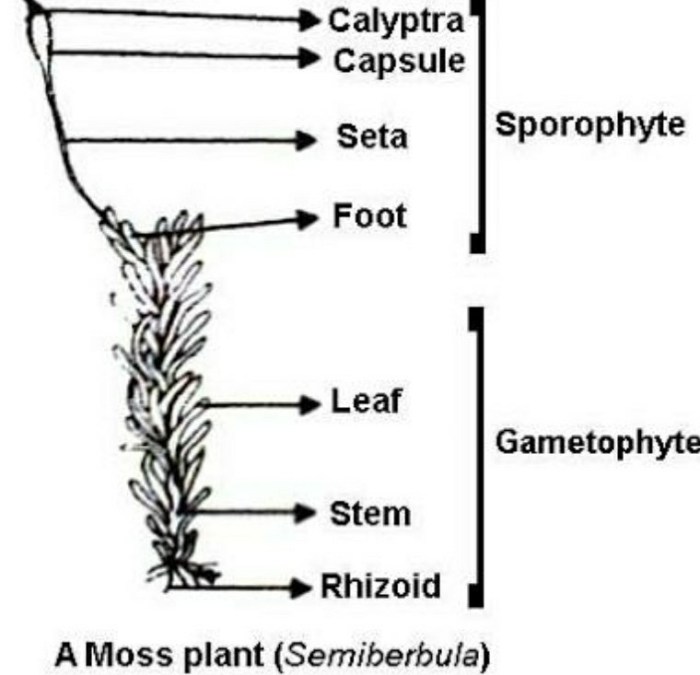
The provided diagram illustrates the intricate structure of a moss, showcasing its various components. Each structure plays a crucial role in the growth, development, and overall functioning of the moss.
Labeling the Structures, Label the structures on this diagram of a moss
- Rhizoids:Root-like filaments that anchor the moss to the ground and absorb water and nutrients.
- Stem:The upright structure that supports the leaves and reproductive structures.
- Leaves:Photosynthetic organs that produce food for the moss through photosynthesis.
- Capsule:A protective structure that houses the spores.
- Seta:A stalk that elevates the capsule above the leaves, aiding in spore dispersal.
- Operculum:A lid that covers the capsule, preventing premature spore release.
- Peristome:A ring of teeth that helps in the dispersal of spores.
- Calypra:A protective cap that covers the young capsule.
Functions of the Structures
- Rhizoids:Anchorage and nutrient absorption.
- Stem:Support and transport of water and nutrients.
- Leaves:Photosynthesis and gas exchange.
- Capsule:Protection of spores.
- Seta:Elevation of the capsule for efficient spore dispersal.
- Operculum:Prevention of premature spore release.
- Peristome:Facilitation of spore dispersal by controlled opening and closing.
- Calypra:Protection of the developing capsule.
Relationships Between Structures
- Rhizoids and Stem:Rhizoids extend from the base of the stem, anchoring the moss and absorbing water and nutrients, which are then transported upwards through the stem.
- Stem and Leaves:Leaves are attached to the stem and are responsible for photosynthesis, providing the moss with energy.
- Capsule and Seta:The seta elevates the capsule, ensuring that spores are dispersed over a wider area.
- Operculum and Peristome:The operculum covers the capsule, preventing premature spore release, while the peristome aids in controlled spore dispersal.
Comparison and Contrast of Structures
| Structure | Function | Size | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhizoids | Anchorage and nutrient absorption | Small and filamentous | Elongated |
| Leaves | Photosynthesis and gas exchange | Small and flat | Variable (e.g., lanceolate, ovate) |
| Capsule | Protection of spores | Small and spherical | Rounded |
| Seta | Elevation of the capsule | Long and slender | Cylindrical |
Top FAQs: Label The Structures On This Diagram Of A Moss
What is the function of the rhizoids?
Rhizoids are root-like structures that anchor the moss to the substrate and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
What is the role of the gametangia?
Gametangia are reproductive structures that produce gametes, the sex cells of mosses.
How do mosses disperse their spores?
Mosses disperse their spores through the air, which are carried by the wind to new locations.